Bullying
When there has been a bullying incident, a clearly defined process is followed.
Once a staff member is aware of a bullying incident,
he or she shall intervene immediately, or as quickly as reasonably possible, to
address the bullying behaviour. The staff member will: stop the behaviour,
identify the bullying behaviours, refer to classroom and/or school rules,
resist the temptation to dismiss the bullying as normal behaviour for that age,
meet with the student(s) separately if necessary, follow-up with appropriate
action, and document the behaviour as well as the action taken at this time.
Head lice
Once head lice is
found, the school has to follow some notification procedures.
The customary
notification for the presence of head lice is to be done on an individual/case by case basis to the parent or guardian of an infested student. Classroom notifications are not done
with typical head lice cases. In the rare case a student is to be excluded, a
notice will be given to the parent in person; a phone contact will be attempted
and documented. If there is concern about the delivery of the notification, it
can be sent by certified mail. A template is available for the School Nurse to
use for this notification. There are even very unusual cases, in which it may
be appropriate to consider a general parent or guardian notification for a high
number of identified cases of head lice.
Eating disorders
Basically, a teacher has to express his care and
concern. If he suspects that one of his students has an eating disorder it is
important that they seek help immediately. The sooner a person starts treatment
for an eating disorder, the shorter the recovery process will be. Seeking help
at the first warning sign is much more effective than waiting until the illness
is in full swing. Some helpful tips when talking to a student he suspects may
have an eating disorder: the teacher has to try to use ‘I’ statements (e.g. ‘I
care about you,’ ‘I am worried about you’). Also, he has to help them to feel
it is safe to talk to him. He has to ask them how they feel, give them time to
talk about their feelings and listen respectfully to what they have to say.
Then, he must encourage them to seek help.
The teacher can help them by remaining supportive,
positive and encouraging. The importance of seeking help early cannot be overstated.
The earlier an intervention occurs, the shorter the duration of the eating
disorder, and the greater the likelihood of full recovery, especially in
children and younger adolescents.
Besides, he has to involve the family whenever
possible. Decisions about when to pass confidential information about a
student’s health and wellbeing on to the student’s parents can be complicated,
but factors to consider in making their decision include the age of the
student, their own thoughts about involving their parents, the severity of the
student’s physical and psychological condition and the resulting level of risk
to their health and safety. Families are generally in a better position than
schools to encourage children and young adults to seek professional medical and
psychological help quickly and on an ongoing basis. It is important that a
student with an eating disorder gets a professional diagnosis.
Violence
Three common procedures to begin assessing school threats: first of all,
teachers should ask what is the motivation of the threat maker and credibility
of the threat. Secondly, they should ask if the threat maker could have the
information on how to carry out the threat. Lastly, they should also ask if the
threat maker could have access to the tools, and the capability to carry out
the threat. Today, we know the answers to questions two and three could easily
be, “Yes.”
Suicide
Basically, the main things to do are
identification and intervention. Early identification and intervention are
critical to preventing suicidal behaviour. When school staff become aware of a
student exhibiting potential suicidal behaviour, they should immediately and
escort the child to a member of the school’s crisis response team for a suicide
risk assessment. They should not “send” the student on their own and typically,
it is best to inform the student what a teacher is going to do every step of
the way. He must solicit the student’s assistance where appropriate. Under no
circumstances should the student be allowed to leave school or be alone.
EMERGENCY PROTOCOL
In the event the fire alarm sounds, a person has to leave the building immediately via the nearest stairway exit.
If possible, before he leaves the room: turn on the lights, open the drapes, close windows and lock the door. Also, he has to remember to wear shoes and carry a towel to place over his nose if smoke is present. If he should happen to be away from his room when the alarm sounds, he must not return to his room itself, but leave the building via the nearest exit.
If a person should spot a fire anywhere in the building, he must activate the building fire alarm system closest to him. If it is possible, without endangering himself, he has to notify someone empowered to keep order and evacuate the building immediately by using the stairs and not the elevator.
Earthquake
During an earthquake, if someone is inside a building, he must stay where he is until the shaking stops. He must not run outside or get in a doorway as this does not provide protection from falling or flying objects, and he may not be able to remain standing. Also, he has to drop down onto his hands and knees so the earthquake does not knock him down. He should drop to the ground. Moreover, this person must cover his head and neck with his arms to protect himself from falling debris. If he is in danger from falling objects, and he can move safely, he should crawl for additional cover under a sturdy desk or table. If there is low furniture or an interior wall or corner nearby, and the path is clear, these may also provide some additional cover. He has to stay away from glass, windows, outside doors and walls, and anything that could fall too, such as light fixtures or furniture. Furthermore, he must hold on to any sturdy covering so he can move with it until the shaking stops. And finally, he has to stay where he is until the shaking stops too.
Airplane
To try to survive a plane crash it is necessary to follow the following tips:
First, the seatbelt must be fastened. Then, the person must place himself in emergency position. He must put the seat upright, rest his head on his knees, grab his ankles with his hands and keep his face between the legs. Anyone should not have a pointed object, since in case of impact it can stick to them accidentally.
Also, everyone have to put their oxygen masks before helping others. In case of depressurization of the cabin the top compartment will be opened and the oxygen masks will go out. People only have fifteen seconds to start breathing through the mask before falling unconscious. After that, a person has to protect himself from smoke. Fire and smoke cause most deaths in air accidents, so he must cover his nose and mouth with a handkerchief or another garment. If possible, he should moisten it for greater safety and try to stay as low as possible from the smoke level when escaping. Later, everyone has to exit the plane as soon as possible. Almost seven out of ten deaths in air accidents occur due to fire, not injuries. That is why it is crucial to get off the plane quickly through one of the emergency exits that a person sees most safely, without entertaining trying to rescue his belongings. Conclusively, everyone must keep in a safe place.
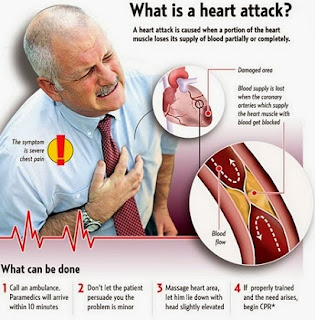
Heart attack
Once it is detected, someone must call for help. If a person has any of these symptoms, he must call his local ambulance service immediately for the safest and quickest transportation to the hospital. He must not drive himself to the emergency room.
Then, in the emergency department, the hospital takes special steps when a person arrives with symptoms of a heart attack. First, the patient is taken to an exam room. Emergency department staff members check the person carefully. The patient is connected to a heart monitor, but this procedure is painless. Oxygen may be given through a tube in the nose and, in the emergency department, the patient is not allowed to eat or drink until a proper diagnosis can be made. He or she must stay in bed to rest the heart as much as possible. In some hospitals, a special team of doctors and nurses arrives to give the best possible care once the patient is diagnosed with a heart attack.








No comments:
Post a Comment